At the point when a site needs to utilize the administrations of another, for example, Bitly presenting on your Twitter stream—rather than requesting that you share your secret key, they should utilize a convention called OAuth.
What is OAuth?
It's critical to see how a program, site, or application may validate you as a client – so they have the correct authorizations? Have you conceded them some kind of method for confirming your identity – and getting to information for your sake? OAuth streamlines this procedure: yet even with robotization, dependably know about how an individual or organization uses your information.
Definition of OAuth
What is OAuth? How OAuth works? OAuth (Open Authentication) is unique access token-based authentication over the internet. OAuth is often used by tech giants to authorize third-party apps to provide access over restricted resources that resides in a giant’s ecosystem without revealing user’s login credentials. OAuth has a large number of scopes or actions that can be requested by third-party apps through APIs hence it is used for easy login in software applications.
Why OAuth was introduced?
OAuth was introduced because there was a need for easy sign-in that could be used as a common sign-in option for lots of apps. All the information required to create a user account is usually present in social media accounts of users so OAuth was developed with the aim to share this information with apps after getting permissions from the user.
When OAuth was launched?
In 73rd Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) meeting in Minneapolis in November 2008, OAuth was introduced to discuss further standardization work to be done. The event was well attended and addressed wide support inside IETF and outsider’s chartering groups. After going through a long development cycle, the OAuth 2.0 Framework and Bearer Token Usage were finally published in October 2012. Although OAuth 2.0 has some limitations like it is not backwards compatible with OAuth 1.0 yet it is being used by Google, Facebook, Twitter, Microsoft’s Azure active directory and many others. OAuth 2.0 provides authorization flows for web apps, desktop apps, mobile phones, and smart devices.
"How to Improve Your Programming Skills?"
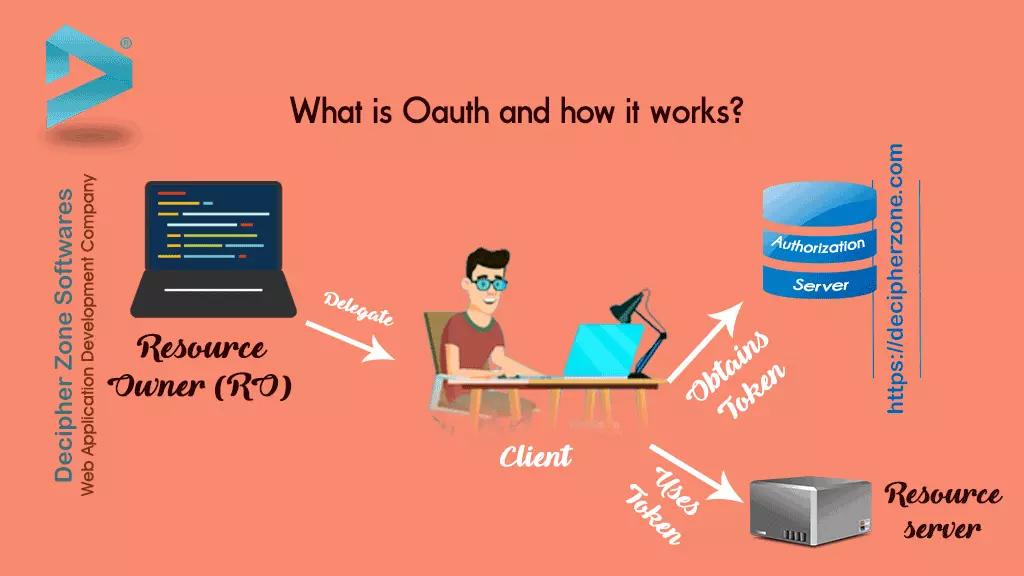
How does OAuth work?
OAuth uses secret keys and access tokens that are uniquely assigned to users for using OAuth for an app developer need to register software applications with the social media platform or the tech giant whose database they want to access. The developer needs to go on developers’ section of the social media platform and register the web app with URL on which it is deployed, then he/she will get the secret keys and access tokens.
OAuth workflow has the following 5 itineraries which are used to authenticate users:
-
User
A visitor who wants easy access over apps without the hassle of creating a new account.
-
Browser
A web browser is a simple tool which is being used by the user to access the software application, here that is called client.
-
Client
The client is a software application which can be a web app, desktop app, mobile phone app or a smart device.
-
Authorization Server
Authorization Server authorizes user and client (software application) from OAuth API provider.
-
Resource Server
When user and client (software application) are authenticated then the user can request for restricted resources through a client (software application) from OAuth API provider.
Workflow of OAuth
-
User visits client (software application) and requests to log in through OAuth of let’s say Facebook.
-
Client (software application) requests a browser for access.
-
Browser redirects access to Facebook’s authorization server.
-
Authorization server asks the user to authenticate himself/herself.
-
The user enters his/her Facebook’s login credentials and authorization server matches the credentials and on the successful match, it authenticates the user.
-
The authorization server then asks the user to authorize the client (software application).
-
User authorizes client (software application) to get data from Facebook.
-
The authorization server redirects the user on the browser to the client (software application) with the authorization code.
-
Client (software application) uses authorization code with credentials (secret key) to request an Access token and refresh token.
-
The client (software application) then goes to the resource server and provides access tokens to get restricted resources from Facebook.
-
Now the user is successfully registered with the app and is logged in to the client (software application).
In how many ways OAuth can be implemented?
OAuth can implement on the front end as well as the backend of software applications so where to implement it is clearly dependent on the scope of software application. In a modern way, JavaScript on the front end is used more for OAuth authentication because there it is easy to manage restrictions on user’s access and the response time is low.