The concept of Software Defined Networks (SDN) has been increasingly embraced in the industry, emphasizing the significance of understanding its fundamental aspects, including its definition, key components, functionality, and advantages. Therefore, in this blog, we will cover every facet of SDN, allowing you to easily grasp its significance.
The evolution of network technology has led to a profound integration of networks with human activities, expanding the scope and reach of the Internet. However, conventional network architectures need help to keep up with the increasing demand for network capacity. This is where Software Defined Networking (SDN) intervenes to support creating a flexible network environment.
Read: A Complete Guide to Quality of Service (QoS) Software
SDN enables organizations to decouple network functionality from physical infrastructure and establish a centralized control plane, allowing for the creation of tailored services and rules to meet diverse requirements. This centralized control plane translates these rules into data flow tables, creating a more flexible and efficient network environment.
Concept of Software Defined Network (SDN)
Software-defined networking (SDN) is a modern network architecture that boosts networking efficiency and flexibility by separating the network control plane from the data plane.
This separation enables dynamic and programmatically efficient network configurations, improving performance and monitoring capabilities. In this way, SDN reflects the principles of cloud computing, offering enhanced scalability, agility, and resource utilization compared to conventional network management methods.
Apart from that, in SDN, software-based controllers or application programming interfaces (APIs) are utilized to interact with the underlying hardware infrastructure and manage traffic flow within the network. This centralized control enables more efficient management and optimization of network resources.
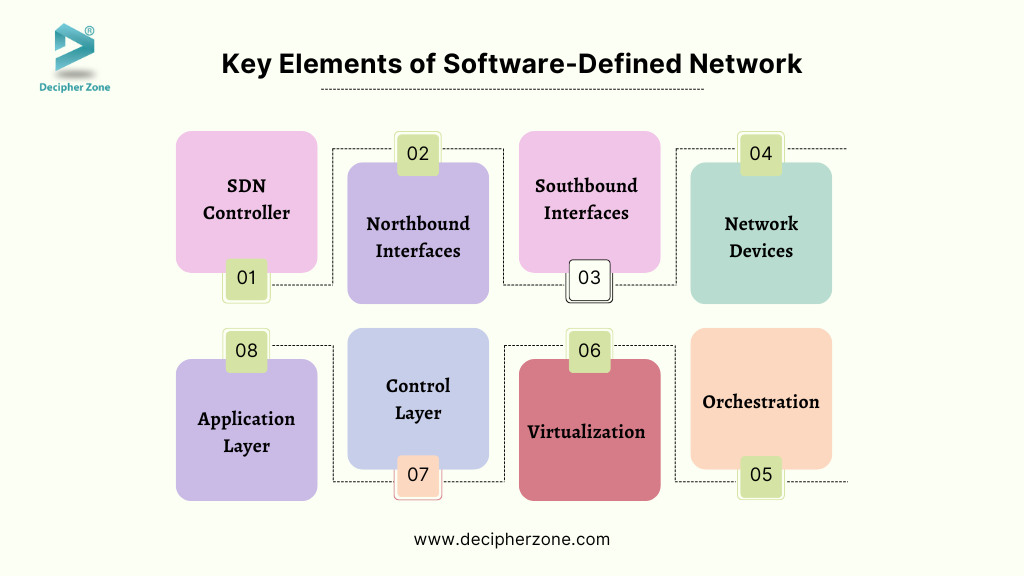
Key Elements of Software-Defined Network Architecture
Software-defined networking (SDN) architecture represents an innovative methodology for network management, delineating the control and forwarding functions to enhance the flexibility and efficiency of network operations.
The key elements of SDN architecture encompass the SDN controller, northbound interfaces, southbound interfaces, network devices, application layer, control layer, virtualization, and orchestration.
-
The SDN Controller functions as the central command center of the SDN architecture. It manages the flow control to the routers/switches using the southbound API and implements application and business logic to establish smart networks through the northbound API. This ultimately enhances application performance and network management. Typically, the SDN controller platform operates on a server and utilizes protocols to direct switches on packet routing.
-
Northbound Interfaces allow the application to communicate with the SDN controller through a web interface or API.
-
Southbound Interfaces allow the SDN controller to interact with network devices through protocols such as OSPF (Open Shortest Path First), SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol), etc.
Read: Radio Frequency (RF) Software Development
-
Network Devices refer to the physical or virtual devices such as switches and routers, that receive and process data from the network controller. They forward traffic based on SDN controller policies, allowing for more coordinated and efficient traffic management.
-
Application Layer is yet another key element of SDN architecture that consists of various network applications running on top of the SDN controller that provide multiple functionalities including but not limited to firewall management, load balancing, and intrusion detection. It allows rapid deployment and development of new network services.
-
Control Layer refers to the logic and policies that govern network behavior. It encompasses the centralized SDN controller software, serving as the brain of the software-defined network. The controller is located on a server and is responsible for managing policies and traffic flows across the network.
-
The architecture of software-defined networking (SDN) often involves virtualization capabilities, allowing for the flexible allocation of network resources and the creation of virtual networks.
-
Orchestration platforms collaborate with SDN controllers to automatically allocate and manage network resources and services.
How Software-Defined Networking Works?
Software-defined networking (SDN) abstracts the underlying infrastructure of the network from the applications, allowing the network to be treated as a single logical entity that simplifies its management while enabling automation. Using a centralized controller, SDN helps handle network configurations and policies from a single point, reducing the complexity of managing individual devices and allowing comprehensive policy enforcement across the network.
The SDN controller can also support dynamic configurations based on real-time demands. Network administrators can use software applications to program and automate network behavior. This programmability allows for rapid deployment of new services and policies, reducing the time and effort required to make network changes.
Read: Media and Entertainment Software Development
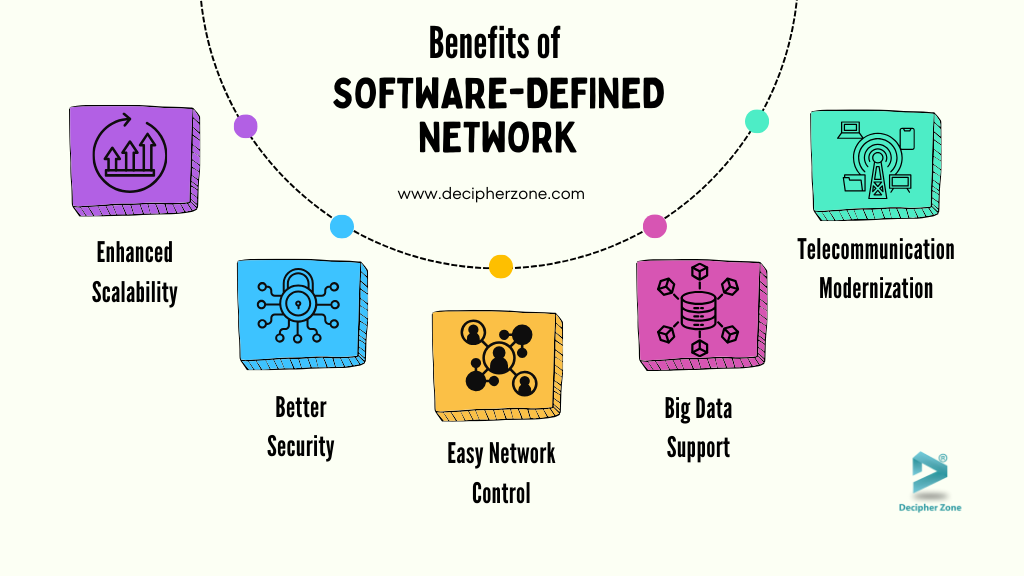
Benefits of Software-Defined Network
Today's services and applications, particularly those involving the cloud, heavily rely on SDN for their operation. The ability of SDN to facilitate the seamless movement of data across different locations is crucial for the functioning of cloud applications. Not only that, but several other advantages make SDN valuable.
Here are a few of them:
-
Scalability: SDN improves the scalability of business operations by allowing the integration of additional devices that support business expansions as required without disrupting the service.
-
Better Security: SDN enables the centralized creation of policies by network administrators to control access and security based on workload type or network segments. Utilizing micro-segmentation can ensure consistency and simplify any cloud network architecture, whether it's public, private, hybrid, or multi-cloud.
-
Ease of Network Control: SDN allows for explicit programming and easier network management by separating the network packet forwarding functions from the data plane. It involves setting up network services on the fly or assigning virtual networks to modify infrastructure from a single centralized location.
-
Big Data Support: Software-defined networking (SDN) provides parallel data processing, efficient management of large volumes of data across multiple locations, and the facilitation of dependable connectivity to handle the ever-expanding data sets that demand substantial data processing capacity.
-
Telecommunication Modernizing: By integrating software-defined networking (SDN) technology with virtual machines and network virtualization, service providers can create customized and flexible network environments for their clients. This capability allows providers to enhance their scalability and offer on-demand bandwidth to accommodate their customers' changing needs and usage patterns.
FAQs
-
What do you mean by SDN network?
Software-defined networking (SDN) is a modern network architecture that boosts networking efficiency and flexibility by separating the network control plane from the data plane.
-
What are the benefits of SDN?
SDN ensures the smooth transfer of data between various locations, which is essential for the effective operation of cloud-based applications. Furthermore, SDN offers numerous benefits, including but not limited to enhanced security measures, support for handling big data, increased scalability, simplified network management, and modernization of telecommunication systems.
-
What are the different SDN models?
Software-defined networking (SDN) encompasses various models that revolutionize network management and control, as follows:
Open SDN: This model leverages OpenFlow to manage switches at the data plane level, enabling centralized network control and programmability.
SDN by APIs: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are used to regulate data flow on individual devices, providing granular control over network behavior.
SDN Overlay Model: This model creates a virtual network on top of existing hardware infrastructure, allowing the deployment of new network services without modifying the underlying physical network.
Hybrid SDN: By integrating SDN with traditional networking protocols, this model enables the support of diverse network functions, combining the advantages of SDN with the reliability of established networking standards.
Conclusion
In recent years, Software-Defined Networking (SDN) has emerged as the preferred choice for numerous network providers. This technology enables providers to streamline operations, enhance security, and modernize infrastructure, leading to improved troubleshooting capabilities.
Read: The Ultimate Guide for Crypto Payment Gateway
In essence, SDN offers a practical solution for businesses seeking to optimize their processes, adapt to changing demands, and scale their operations without being bound by the limitations of traditional network infrastructure.
If you are in search of SDN experts to assist you in integrating SDN within your business, do not hesitate to reach out to our team of professionals today!

