Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing. If you are into software programming and everything in between, you must have heard about cloud computing and edge computing.
According to the Grand View Research report, even the cloud computing market size is expected to reach a whopping $1554.94 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 14.1%. Based on the report from Globe Newswire, the edge computing market size is about to reach $157.91 at a CAGR of 37.9% by 2030.
But do you know what cloud and edge computing refers to, how they differ from each other, and help businesses? To help you out, we will cover everything from definitions to advantages and differences in this blog.
Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing: Definition
What is the difference between Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
Read: Comprehensive Guide to Edge Computing
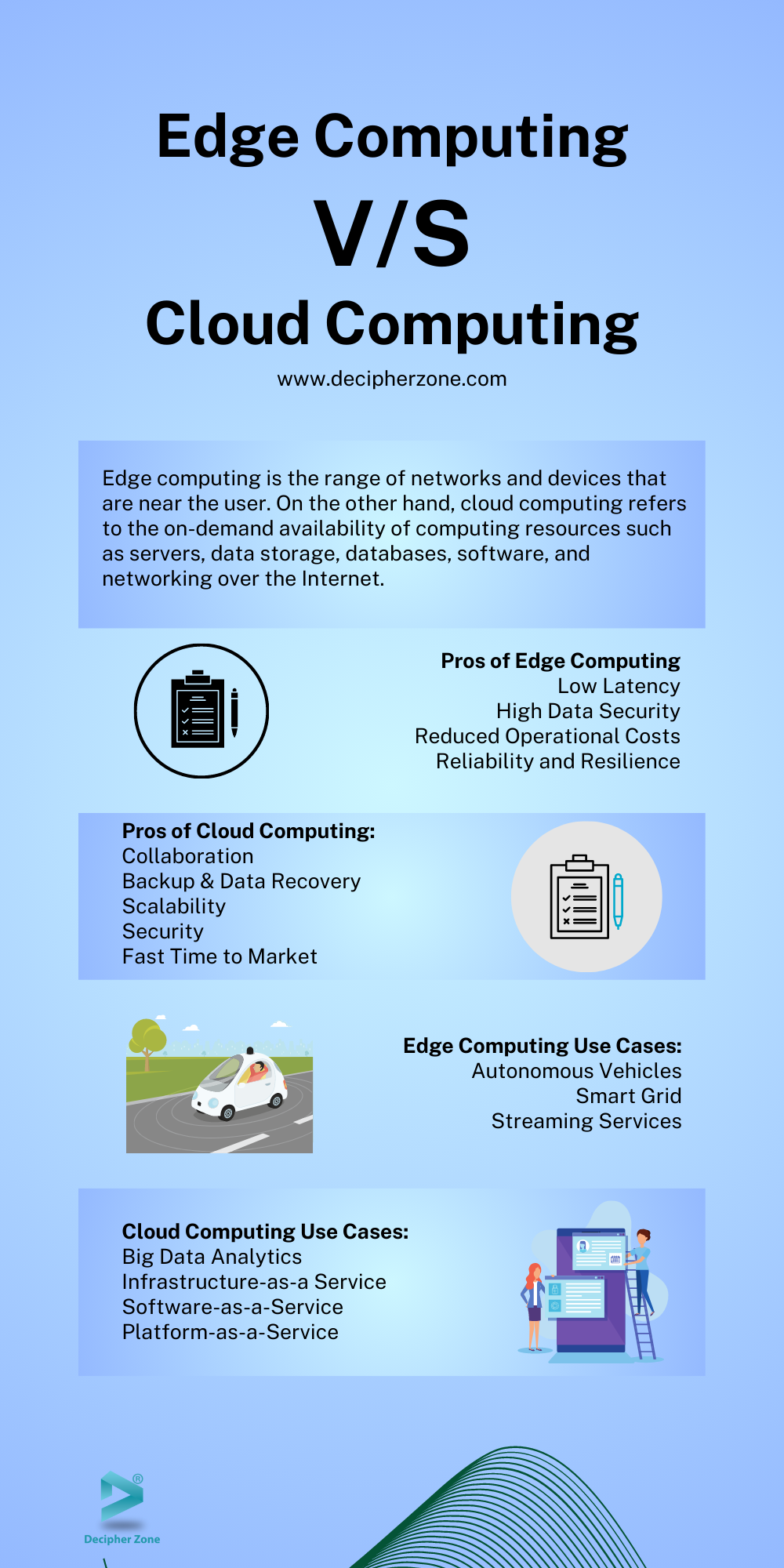
Edge Computing refers to the distributed computing paradigms. It brings data and storage closer to the data sources. Put simply, it is the range of networks and devices that are near the user. By bringing data closer to the source, edge improves data processing speed and volume, enabling real-time results.
Read: Cloud Application Development
Cloud Computing refers to the on-demand availability of computing resources such as servers, data storage, databases, software, and networking over the Internet. Cloud computing service providers store and process data in a separate location from the users. With cloud computing, you can save files on remote servers and retrieve them whenever needed.
Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing: Pros
With the basic knowledge of edge computing and cloud computing, let’s move ahead and look at the pros of each.
Read: What is Cloud Migration
Pros of Edge Computing:
-
It eliminates the need to move data from the source to the cloud and back, significantly reducing latency and serving faster response times.
-
As the data is kept out of the centralized network and closer to the edge, it can also improve data privacy and security for the users.
-
With a minimal requirement to transfer data to the cloud, edge computing can reduce the operational costs of any organization.
-
Edge helps in fetching and processing data even if the internet connectivity is weak, improving the reliability of the connected systems.
-
Edge also reduces central point failure of the system to further improve resilience.
Pros of Cloud Computing:
-
With cloud computing, you only pay for the used resources, avoiding data center overprovisioning.
-
Irrespective of the location, cloud computing allows employees to communicate and collaborate in real time with an active internet connection.
-
Cloud service providers also offer disaster recovery and backup capabilities to prevent the loss of data in case of malicious threats or hardware malfunction.
-
You can also scale cloud infrastructure based on fluctuating workloads.
-
Cloud computing infrastructure also comes with encryption, virtual private clouds, and API keys that help in securing an organization’s data.
-
Developing software in the cloud helps developers increase development speed with quick deployments, making it easier to test and design new applications and market them.
Read: Guide To Perform A Cloud Backup
Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing: Cons
Now that we know about the pros of edge and cloud computing, it is time to understand their limitations.
Cons of Edge Computing:
-
The physical infrastructure of edge computing limits the resources which makes it difficult to scale them as per demands.
-
Being a decentralized system, edge computing can require users’ attention and are also less reliable.
-
Maintaining, integrating, and upgrading the infrastructure of edge computing systems is complex and requires skilled professionals.
-
Different edge systems might not be compatible with one another, making it difficult to integrate multiple devices into one edge computing solution.
Cons of Cloud Computing:
-
Cloud computing systems highly rely on internet connectivity which makes it difficult to access data on servers with bad internet connection.
-
Storing sensitive data in the cloud can be risky if strict security measures are not taken.
-
Cloud computing can sometimes also lead to vendor lock-in, integration complexity, and minimal control over cloud infrastructure.
Read: Cloud Application Development
Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing - Use Cases
Although you know the definition, pros, and cons of edge and cloud computing, it is important to learn about their use cases as well. Here we have enlisted a few use cases of both edge computing and cloud computing.
Edge Computing Use Cases:
-
Autonomous Vehicles: Using the cloud for real-time analysis of self-driving cars can be quite unsafe due to the potential for latency. On the other hand, using edge computing in autonomous vehicles helps collect vast information and make real-time decisions based on them ensuring passengers’ safety.
-
Smart Grid: IoT devices and sensors connected with edge systems in offices or factories can assist in monitoring energy consumption and analyze it in real-time to make better decisions and improve the amount of green energy an organization consumes.
-
Streaming Services: Integrating edge computing in content delivery or video streaming can reduce latency while enabling a better user experience. It can also offer personalized experiences, content suggestions, etc.
Cloud Computing Use Cases:
-
Big Data Analytics: As big data companies need massive storage, processing, analysis, and security, implementing cloud computing can help them better manage and understand data to optimize their customer experience.
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): It provides virtualized infrastructure computing resources over the internet. IaaS can be used by organizations for hosting a website or testing an app development environment.
-
Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS refers to the cloud computing model where software is licensed and delivered to the users on a subscription basis. Put simply, it allows organizations to host their software in the cloud and make it easily accessible through a browser and an active internet connection. Some of the major benefits of SaaS are lowered upfront costs, ease of use, and subscription-based pricing.
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS): It is another model of cloud computing that provides capabilities to manage applications, host development kits, and other tools to build, deploy, and market their applications. Using PaaS, companies can save a ton of money by simply outsourcing database security, hosting, and data storage.
Conclusion
We hope this blog helped you understand the similarities and differences between edge computing and cloud computing. Needless to say, both technologies have equal importance in the industry and no one is going to abandon one for another. Even industry experts are looking for ways to employ both cloud computing and edge computing to overcome any limitations these technologies have.
And if you also want to incorporate cloud computing, edge computing, or both in your business, then get in touch with our experts and share your requirements. We will provide you with the best solutions that meet your requirements while staying within your budget.
So what are you waiting for? Get in touch with us now!
FAQs: Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing
What is an example of edge computing?
Fleet management, remote monitoring, wearable devices, safety monitoring, etc. are some real-life examples of edge computing.
What are edge computing and cloud computing?
Edge computing is the range of networks and devices that are near the user. On the other hand, cloud computing refers to the on-demand availability of computing resources such as servers, data storage, databases, software, and networking over the Internet.
Will edge computing eventually overtake and replace cloud computing?
As both technologies serve different purposes, the likelihood of edge computing overtaking cloud computing is extremely low.

