What is the proxy design pattern in Java? The object oriented Proxy Design Pattern is a structural design pattern which is concerned with how classes and objects compose to form larger structures. The proxy design pattern in java takes a similar approach by providing a proxy object that acts as a placeholder for another object. Commonly a proxy is a class that functions as an interface to something else. The proxy design pattern can be best understood with the help of a real-world example. In computer networks, we usually come across the term proxy server. It is a server application that acts as an intermediary for web requests from the clients. The client, instead of connecting directly to a server, directs its request to the proxy server which performs the intended filtration and other network transaction. The purpose of proxy server is to simplify and control the complexity of the requests by providing additional benefits such as privacy and security. Proxies have been designed to add structure and encapsulation to distributed systems in computer networks.
The Proxy Design Pattern has the same intent has the proxy servers in computer networks. In this article we will define what is proxy design pattern, walk through the implementation and also see what are the benefits of using the proxy design pattern in java.
What is Proxy Design Pattern in Java?
What is the Proxy Design Pattern in Java? The Proxy Design Pattern provides a representative for another object in order to control the client’s access to it. The intent is to provide a placeholder for that object to control access to it. The literal meaning of proxy is “the authority” to represent someone else”. Now, that says a lot of things about the design pattern itself. As exemplified in the introductory paragraph, the proxy could interface to anything, it can be an interface to a network connection, an object in memory, a file or any other resource that is expensive to duplicate. The purpose of the proxy in the object oriented proxy design pattern is to act as a wrapper that is called by the client to get access to the intended object.
Read: "What is the Iterator Design Pattern?"
The proxy design pattern can be used in cases where the cost of creation and maintenance of an object is expensive for the application. It can be used to defer the full cost of its creation and initialization until we actually need it. An example for it could be an application that is slow to load, and our task is to make the loading faster. One way could be to avoid creating all the expensive objects at once when the document is opened. The only way to approach this would be to create expensive objects on demand. The proxy can be a great solution for this, it can act as a stand-in object for the real object the proxy would act just like the real image and would instantiate it when required.
Read: "What is facade design pattern in Java?"
Another example we can take is of the same application, we not only want our application to load faster but we need the resources inside of it to be fast as well. The proxy can be of great help here as well, we can provide extra functionality inside of it like caching when operations on real objects are resource intensive. The proxy design pattern examples in java have been used a lot to give you deep insights on this object oriented proxy design pattern. Now it is time to dive into a code example of proxy design pattern in java.
Proxy Design Pattern Example in Java
In our example we are going to use a simplified version of loading a video file using the proxy design pattern in java. We are going to demonstrate two things:
-
How the proxy behaves as a representative to the actual object?
-
A simplified version of caching.
Before diving into the code example lets take a look at the participants required to make use of the proxy design pattern.
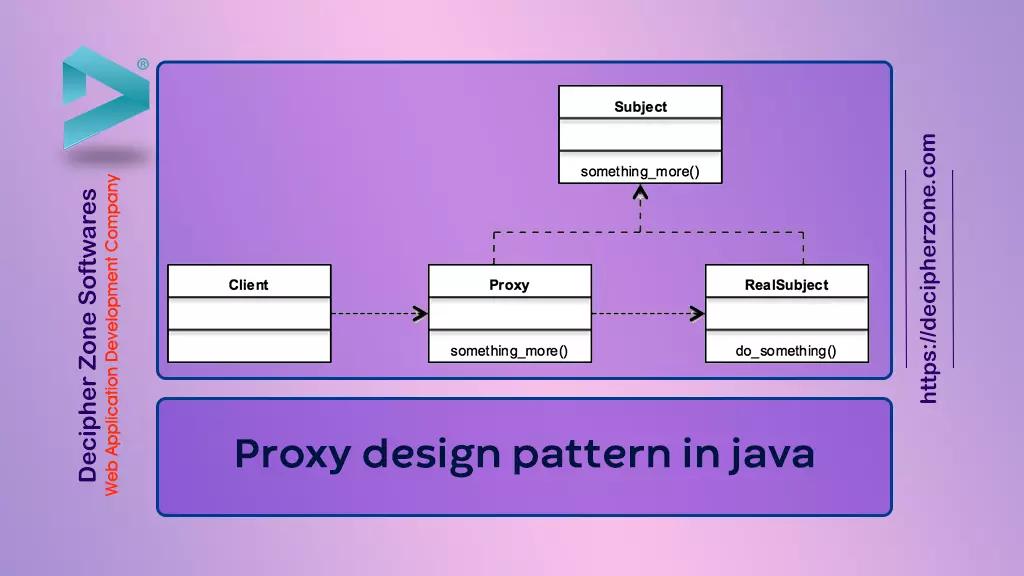
- Proxy
The Proxy maintains a reference that lets it access the real subject. It provides an interface identical to the subject’s interface so that a proxy can easily be substituted for it. The Proxy controls access to the real subject and it may also have the responsibility of creating and deleting the main object (subject).
- Subject
Subject can be thought of the main object that acts a common interface for Proxy and the object that implements its interface.
- RealSubject
It defines the real object that is represented by the proxy.
The usage of these participants will be clear with the following code example.
1. The Video Interface
The Video Interface provides a structure for the proxy and RealVideo class to implement.
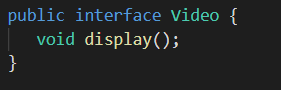
Fig: proxy design pattern in java : Video Interface
2. The RealVideo Class
The RealVideo class represents a video file object that the application will load. It overrides the method from the Video interface. However, the RealVideo instance would not be directly used by the client, it will only be done through the proxy.
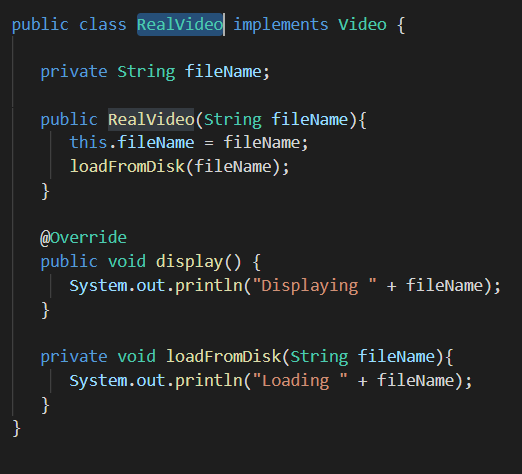
Fig: proxy design pattern in java : RealVideo (RealSubject)
3. The Proxy (ProxyVideo)
ProxyVideo implements the same interface (Video) as the RealVideo class. Note that the RealVideo is the RealSubject and Video interface is the subject. The client requests for the video file through the Proxy itself.
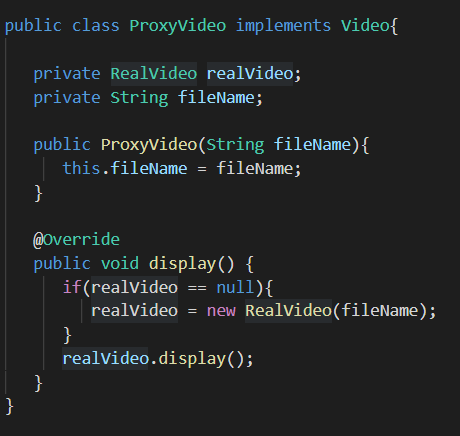
Fig: proxy design pattern in java : Proxy (Proxy Video)
4. Putting It all Together (Proxy Design Pattern Demo)
The client which is the ProxyPatternDemo class in our case requests a video file from the proxy. The proxy then delegates the instantiation of the video file to the RealVideo object. The first time the request is made, the video will be loaded from disk. The second time it will not be loaded from disk because we have cached it inside the realVideo variable.
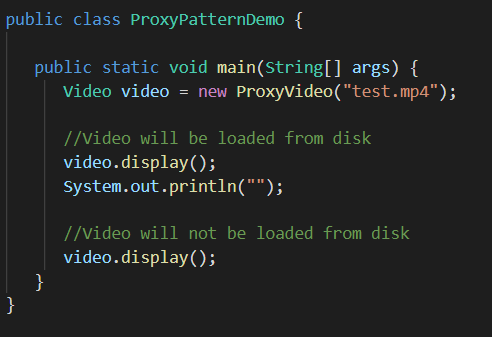
Fig : proxy design pattern in java : ProxyPatternDemo
What is the consequence of using proxy design pattern example in java?
- We have introduced a level of indirection when accessing the RealVideo object. Our code example is optimised to create an object on demand and also cache it i.e. once loaded we do not have to access the memory to use it again.
- We have introduced an object that manages interaction between client and the remote object (RealVideo).
- The proxy design pattern avoids duplication of objects which may be memory intensive. This in turn increases the performance of the application.
- One drawback of this design pattern is that like any wrapper, it will increase the number of classes and objects in our designs.
Read: "When to Use Composite Design Pattern in Java"
If you have ever come across the decorator design pattern, you may find it similar to the proxy design pattern. Although they have similar implantation as proxies, the purpose of decorators is slightly different. A decorator adds one ore more responsibilities to objects whereas a proxy controls the access to an object.