Explore the world of blockchain technology, a strong solution for safeguarding and managing your data in the modern digital landscape. Understand the definition, advantages, and various types of blockchain technology to fully comprehend its potential impact on data security and management. Utilize blockchain technology to improve security, streamline processes, and boost productivity.
Blockchain technology is known for its ability to provide a high level of security, transparency, and traceability in digital transactions. By implementing blockchain technology, organizations cannot only enhance the security of their network but also improve transaction processing speeds.
The versatility of blockchain technology allows it to be applied across a wide range of industries and sectors, making it a valuable solution for various business needs. To gain a comprehensive understanding of the different types and applications of blockchain technology, we encourage you to delve into this article for detailed insights.
Read: Blockchain Digital Identity
Quick Brief on Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology enables a transparent exchange of information in a corporate network through an advanced database method. The database utilizes interconnected blocks to store data in a chain. Since the chain needs approval from the network to be changed or deleted, the information stays reliable and unchanged over time.
By leveraging blockchain technology, an unchangeable and immutable ledger can be created to track orders, payments, accounts, and other transactions. The built-in system features prevent unauthorized transaction inputs and ensure uniformity in the shared view of these transactions.
4 Different Types of Blockchain Technology
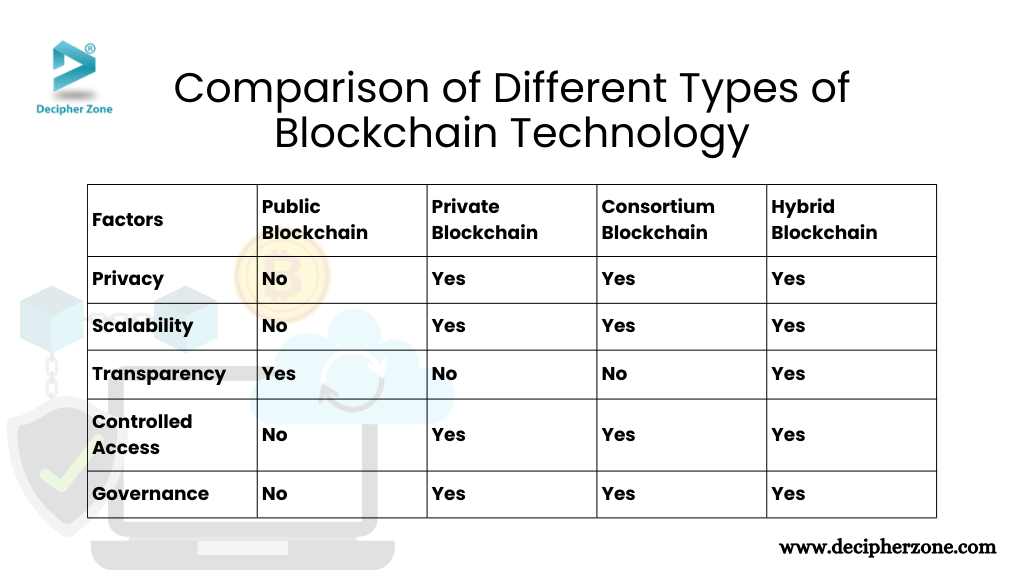
Blockchain technology can be categorized into Public, Private, Consortium, and Hybrid, depending on the organization's structure and governance. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, which significantly influence its optimal applications. Here's an in-depth overview of the different types of blockchains and the fundamental components of each network.
1. Public Blockchain
Public blockchains are popular for their easy access, decentralized nature, and various uses. They are often associated with cryptocurrencies and are created through a process called "mining". In this process, nodes on the network are rewarded with new cryptocurrencies for solving complex mathematical equations.
However, not every public blockchain is used for virtual currency. Some are used to provide different ways of handling transactions for financial services, such as smart contracts or programmable money like Ethereum. Public blockchains are also called “permissionless” because the protocol itself doesn't have access control. This means that anyone with an internet connection can download and run a node on a public blockchain. This allows them to interact with other nodes.
Pros: Secure, Trustable, Fully decentralized, Transparent.
Cons: Scalability, High energy consumption, slow processing speed.
2. Private Blockchain
A private blockchain is the most restricted form of blockchain access. It is controlled by an organization, organizational chart, or individual. Users of this blockchain have limited visibility and cannot access transaction details. Private blockchains are commonly used by major corporations, such as banks, to handle sensitive data and protect it from competitors.
Information stored on private blockchains requires permission from an authorized person within the company for viewing. Private blockchains resemble early internet intranets, which were primarily used within companies to provide secure access to information that was not yet available on the World Wide Web.
Pros: Speed, Scalability, Privacy.
Cons: Centralized, Security, Difficult to trust.
3. Consortium Blockchain
In a consortium blockchain network, there are multiple "nodes" or "members" in the network. These members establish a peer-to-peer network, which is utilized to validate transactions and ensure the accuracy and permanence of transaction records. The blockchain also diminishes the necessity for third-party intermediaries, as the involved parties can directly verify each other through their computers.
The consortium blockchain serves as an efficient solution when a group of interconnected businesses seeks to collaborate in maintaining a shared ledger but may not completely trust each other. For instance, when several companies in a supply chain need to monitor products from start to finish, creating a shared blockchain may be more effective than establishing independent blockchains for each business involved in the process.
Pros: Low transaction cost, Privacy, Faster growth, Resilience, Flexibility.
Cons: Confidentiality is often compromised, Secure inter-ledger communication, Transparency.
Read: Top 8 Benefits of Blockchain Technology
4. Hybrid Blockchain
A hybrid blockchain blends the characteristics of both public and private blockchain technology. It is supervised by a central authority, with a private, permission-based system operating alongside a public system. This setup enables the central authority to regulate which specific data is accessible to the general public. However, authorized users can validate them through a smart contract system when needed.
Moreover, the private entity managing a hybrid blockchain system is unable to alter or manipulate transactions on the blockchain. Organizations seeking the advantages of both public and private blockchains favor a hybrid blockchain system. For example, companies in heavily regulated industries, such as banking, often choose this type of system.
Pros: Integrated various features, High transactions, eagles asset digitalization, Allows private transactions.
Cons: Complexity, Not fully decentralized.
Advantages of Blockchain technology
Blockchain technology provides various benefits to different sizes of businesses and individuals such as:
.png)
High Level of Security
The use of cryptographic techniques in blockchain technology enhances security. All transactions are interconnected, making them easy to trace, preventing fraud, and resisting tampering. This ensures that sensitive information and assets are protected from unauthorized access and cyber-attacks, reducing the likelihood of misuse commonly observed in centralized systems.
Transparency
Since every transaction is traceable and interconnected, they are visible to all the involved parties, which fosters a high level of trust. This is particularly advantageous for financial and public sector organizations, where being accountable is crucial. Blockchain creates a transparent system where activities can be monitored and confirmed by users, ensuring transparency and integrity.
Immutability
The immutability of blockchain is vital for its security. Once data is recorded, it becomes extremely difficult to change, ensuring the integrity of your information and protecting it against tampering and fraud. Immutability provides businesses with reliable data storage, essential for legal compliance and record-keeping.
Enhances Efficiency
Blockchain technology streamlines and speeds up processes, improving overall efficiency. In certain cases, traditional methods can be time-consuming, for example, in international payments and real estate transactions.
Although there may be some trade-offs in terms of security or decentralization, these private and hybrid chains effectively reduce the need for intermediaries, pushing the boundaries of blockchain efficiency.
As the industry progresses, these innovations are paving the way for public blockchains to catch up and eventually tackle the blockchain trilemma – balancing scalability, security, and decentralization simultaneously for the benefit of the entire ecosystem.
Read: Role of Blockchain in Fintech
Conclusion
Blockchain is a revolutionary technology with numerous benefits. It ensures high security, transparency, cost-efficiency, and faster transactions. Its versatility makes it suitable for various industries such as banking and supply chain tracking. Essentially, blockchain has the potential to significantly transform many sectors. Embracing blockchain positions your business at the forefront of innovation, guaranteeing secure and streamlined operations.
For your blockchain solution, let our proficient team at Decipher Zone create the design, development, and implementation. We strive to deliver development that aligns with your exact requirements. Allow us to alleviate your concerns by transforming your idea into a profitable product. Whether you require an MVP or need to revamp an existing product, we will create a solution that captivates your users.
FAQs
-
How does blockchain improve security?
Blockchain technology has a decentralized structure and the use of cryptographic algorithms creates a highly secure environment by making it extremely difficult to tamper with data.
-
Can blockchain technology increase efficiency in business processes?
Blockchain technology has the capability to automate and modernize various processes by creating transparent and secure digital records. Through the use of decentralized ledgers, blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as banks or clearinghouses, which can result in faster and more cost-effective transactions. Additionally, blockchain's ability to provide a tamper-proof record of transactions can enhance security and trust in various industries.
-
What are the most important components of Blockchain technology?
The key elements of a blockchain include decentralization, immutability, and consensus mechanisms. Decentralization guarantees that the network is not controlled by a single entity, thereby increasing security and minimizing the potential for tampering. Immutability involves the inability to modify past transactions once they have been recorded on the blockchain, ensuring reliability and openness. Consensus mechanisms are protocols that ensure unanimous agreement among all network participants regarding transaction validity, establishing trust and enabling the creation of a single, shared version of truth.

