Network Function Virtualization (NFV) refers to the process of decoupling network functions from traditional hardware and allowing them to run as software on virtual machines, saving time and money for organizations. Leveraging NFV, businesses can effortlessly adapt to the changing market needs in more agile and cost-effective ways.
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) has emerged as a revolutionary concept in the ever-evolving digital landscape. It has transformed how networks are designed, deployed, and managed. In fact, the NFV market size is expected to grow at a CAGR of 18.9% and reach a whopping USD 134.4 billion by 2032, making it the perfect time to learn about NFV and how it can benefit your business.
In this blog, we will break down the complexities surrounding NFV technology to help you better understand how it reshapes the network landscape.
What is Network Function Virtualization?
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is a modern network architecture model that aims to enhance the flexibility and efficiency of networks by substituting traditional network appliance hardware with virtual machines (VMs).
In NFV, a hypervisor is employed to operate networking software and processes within the virtualized environment, including routing, proxies, load balancing, and other network functions. This approach allows for greater scalability, cost savings, and agility in managing and deploying network services.
Read: What is Network Analysis?
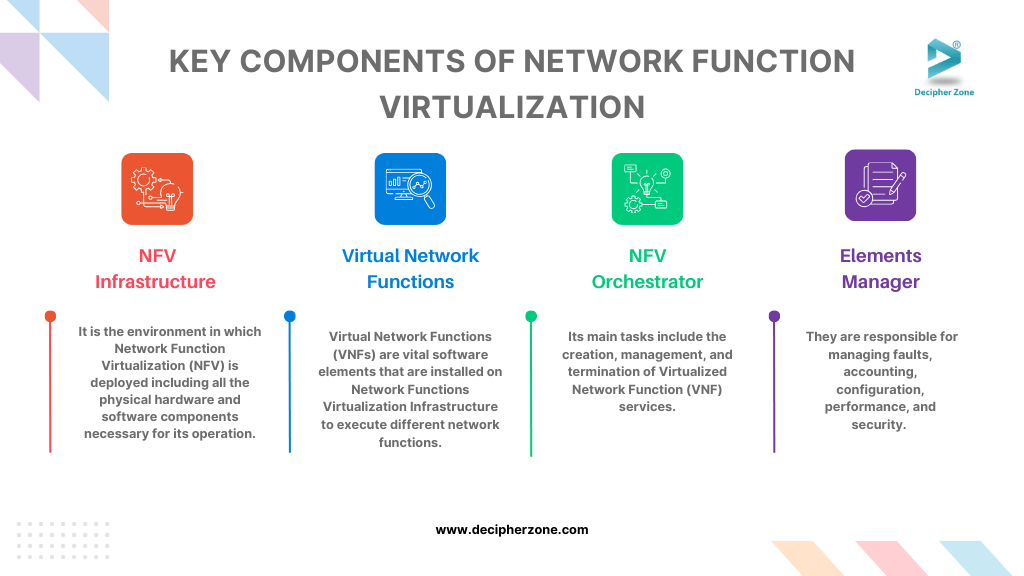
Key Components of Network Function Virtualization
The network function virtualization model is built on several components that are essential for its operation and functionality. These components are as follows:
-
Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI)
The environment in which Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is deployed includes all the physical hardware and software components necessary for its operation. NFV that extends across multiple geographical locations and the networking equipment that facilitates connectivity between these locations is considered part of the NFV Infrastructure (NFVI).
-
Virtual Network Functions (VNFs)
Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) are vital software elements that are installed on Network Functions Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI) to execute different network functions. Some of these network functions that are implemented in the NFVI include software-defined wide area network (SD-WAN), firewalls, enforcing Quality of Service (QoS), and routing capabilities.
-
NFV Orchestrator
The NFV orchestrator plays a critical role in the virtualized network environment by taking on several key responsibilities. Its main tasks include the creation, management, and termination of Virtualized Network Function (VNF) services. It is also responsible for overseeing the management of NFVI resources, which encompasses networking, storage, and computing resources.
An essential aspect to note is that the NFV orchestrator does not handle these responsibilities in isolation; rather, it collaborates closely with the Virtual Network Function Manager (VNFM) and the Virtual Infrastructure Manager (VIM) to effectively carry out its functions.
-
Element Managers
Element managers are crucial parts of NFV, as they function as the management system for virtual network functions. They are responsible for managing faults, accounting, configuration, performance, and security. It's worth noting that a single element manager can handle multiple virtual network functions, whereas a virtual network function can use one element manager when required.
Why Network Function Virtualization?
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is vital for businesses looking to transition to virtual machines while abstracting from physical resources. NFV enables the virtualization of functions such as firewalling and routing by separating communication services from dedicated hardware.
Read: What is Function-as-a-Service (FaaS)
Unlike traditional networking, which can take months to deploy, NFV allows for the rapid deployment of network components in just a few hours. Additionally, the virtualized services operate on a cost-effective, pay-as-you-go model, reducing operating expenses and improving the scalability of the network architecture.
How does Network Function Virtualization Work?
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) works by substituting hardware networking elements with virtual machines for executing software that conducts the equivalent networking tasks as conventional hardware. These tasks encompass routing, load balancing, and firewall security.
Utilizing a hypervisor or software-defined networking controller enables network administrators to instruct various virtual network segments and streamline network management. Employing virtualization, IT managers can set up different network functions through a single interface rapidly.
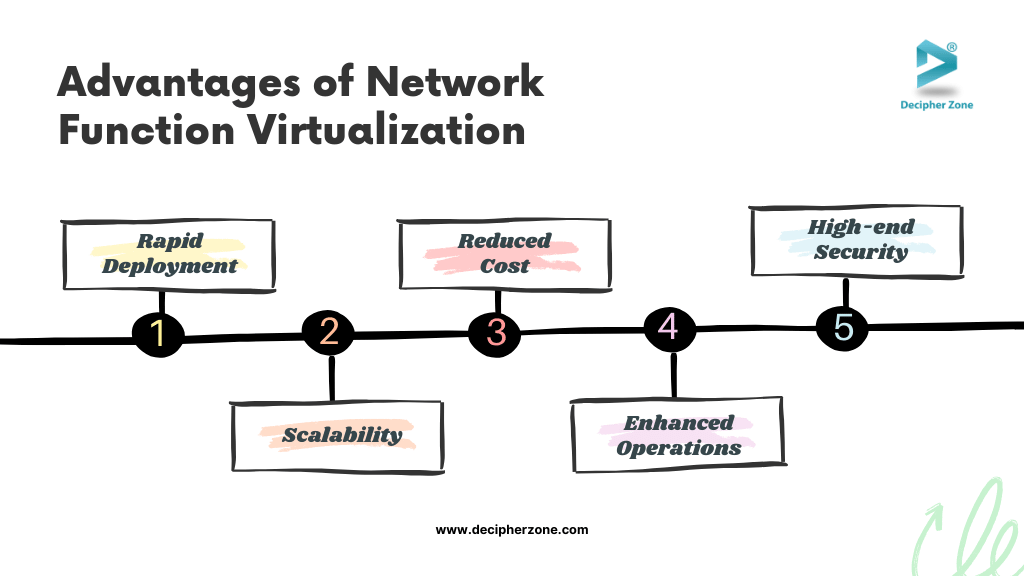
Network Function Virtualization Advantages
Adopting network function virtualization (NFV) can bring several advantages to an organization, a few of which are listed below:
-
Rapid Deployment: With NFV, organizations can rapidly deploy new network functions and services to quickly adapt to business needs without any specialized hardware.
-
Scalability: Network Function Virtualization enables easy scaling of network services up and down to match changing needs.
-
Reduced Cost: By eliminating the dependence on conventional hardware, NFV reduces space requirements, power consumption, and maintenance costs for network functions and services.
-
Enhanced Operations: NFV simplifies the transfer of remote network components from one location to another by aggregating company-wide network functions in software form, thus removing the reliance on on-premise network functions.
-
High-end Security: NFV improves network security by integrating standard virtualized security gateways for server environments. Furthermore, NFV implements virtualized security measures, including encryption, intrusion detection, anti-malware, and security protection for agile and cost-efficient network security.
Challenges and Solutions of Network Function Virtualization
Regardless of the benefits that Network Function Virtualization (NFV) offers, it also presents certain challenges that businesses must overcome. Therefore, below, we provide some major challenges and their solutions when adopting NFV.
Read: Types of Programming Paradigms
Challenge I
When virtualized network functions are subjected to high workloads, they may experience performance issues compared to dedicated hardware devices.
Solution: To address this challenge, it is recommended to implement techniques such as Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV), Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK), and Virtio. These approaches can help improve the performance of virtualized network functions and mitigate any issues that may arise during high workloads.
Challenge II
Compared to traditional hardware devices, managing virtual network functions can be complex and time-consuming.
Solution: To overcome the management complexity of the VNF, leverage orchestration tools such as NetBrain, SolarWinds, Puppet, or Ansible. These tools will help you automate the virtual network function’s deployment, management, and scaling.
Challenge III
It can be difficult to integrate VNF from various vendors and can become a threat to NFV interoperability.
Solution: For handling the interoperability challenge in the network function virtualization, enable interoperability testing and foster open standards that will make the interoperability between NFV vendors and components efficient and smooth.
Wrapping it Up
In conclusion, it is expected that network function virtualization (NFV) will gain traction and be adopted in the future. NFV is projected to be in high demand in areas such as 5G networks, cloud architecture, artificial intelligence, automation, and edge computing. This makes it an opportune time to invest in NFV to enhance scalability and customization while minimizing on-premise infrastructure dependencies as it is the most sanguine trend in virtualization.
If you want to transition from traditional, space-consuming, and costly hardware infrastructure to cost-effective and advanced virtual environments for managing your daily business operations, Decipher Zone is the ideal choice.
Read: Serverless vs Containers
You can reach out to our experts, discuss your requirements, and receive a personalized quote tailored to your business needs and future objectives for digitally transforming your operations.
FAQs
-
What does network function virtualization mean?
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is a modern network architecture model that aims to enhance the flexibility and efficiency of networks by substituting traditional network appliance hardware with virtual machines (VMs).
-
What is the use case of NFV?
NFV is utilized to replace traditional hardware network functions such as routing, proxies, load balancing, and other network functions with virtual machines.
-
What are the benefits of network function virtualization?
Network function virtualization (NFV) can bring several advantages to an organization such as rapid deployment, scalability, reduced costs, enhanced operations, and high-end security.

